Flat (music)
In music, flat means lower in pitch. It may either be used in a general sense to mean any lowering of pitch, or to specifically refer to lowering pitch by a semitone. A flat is the opposite of a sharp (♯) which indicates a raised pitch in the same way.
| ♭ | |
|---|---|
Flat (music) | |
| In Unicode | U+266D ♭ MUSIC FLAT SIGN (♭) |
| Different from | |
| Different from | U+0062 b LATIN SMALL LETTER B |
| Related | |
| See also | U+1D12B U+266F ♯ MUSIC SHARP SIGN |
The flat symbol (♭) appears in key signatures to indicate which notes are flat throughout a section of music, and also in front of individual notes as an accidental, indicating that the note is flat until the next bar line.
Pitch change
[edit]The symbol ♭ is a stylised lowercase b, derived from Italian be molle for "soft B" and German blatt for "planar, dull". It indicates that the note to which it is applied is played one semitone lower. In modern tuning this corresponds to exactly 100 cents.[1][2]
In traditional and modern microtonal temperaments the difference in pitch indicated by a sharp or flat is normally smaller than the diatonic semitone of standard modern tuning. In those tuning systems, the size of the shift made by the ♭ symbol usually conforms to the smaller-sized lowering of pitch;[a] however, for some tuning systems it may instead be replaced by a different symbol for raising and lowering pitch, depending on the author's preference and the intricacy of any microtuning involved.[b]
Related symbols
[edit]A double flat (𝄫) lowers a note by two semitones, or a whole step.
A quarter-tone flat, half flat, or demiflat indicates the use of quarter tones; it may be marked with various symbols including a flat with a slash (![]() ) or a reversed flat sign (
) or a reversed flat sign (![]() ). A three-quarter-tone flat, flat and a half or sesquiflat, is represented by a demiflat and a whole flat (
). A three-quarter-tone flat, flat and a half or sesquiflat, is represented by a demiflat and a whole flat (![]() ).
).
The symbols -, ↓, ![]() , among others, represent comma flat or eighth-tone flat, or a quarter of a flat (not to be confused with the larger quarter tone).[c]
, among others, represent comma flat or eighth-tone flat, or a quarter of a flat (not to be confused with the larger quarter tone).[c]
A triple flat (♭𝄫) is very rare.[3] As expected, it lowers a note three semitones, or a whole tone and a semitone. (For example, B♭𝄫 is enharmonic with A♭.)[4]
Flats in key signatures
[edit]| Order of flats in key signatures | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The order of flats in key signatures is
- B♭, E♭, A♭, D♭, G♭, C♭, F♭.
The corresponding order of keys also follows the circle of fifths sequence:
- F♮, B♭, E♭, A♭, D♭, G♭, C♭.
Starting with no sharps or flats (C major), adding the first flat (B♭) indicates F major; adding the next (E♭) indicates B♭ major, and so on, backwards through the circle of fifths.
Some keys (such as C♭ major with seven flats) may be written as an enharmonically equivalent key (B major with five sharps in this case). In rare cases, the flat keys may be extended further:
requiring double flats in the key signature. These are generally avoided as impractical, and the simpler, equivalent key signature is used instead. This principle applies similarly to the sharp keys.
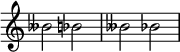
Key signature example
[edit]The staff below shows a key signature with three flats (E♭ major or its relative minor C minor), followed by a note with a flat preceding it: The flat symbol placed on the note indicates that it is a D♭.
In 12 tone equal temperament ( 12 TET )[d] lowering a note's pitch by a semitone results in a note that is enharmonically equivalent to the adjacent named note. In this system, B♭ and A♯ are considered to be equivalent. In other, non-standard tuning systems, however, this is not the case.
Accidentals
[edit]Accidentals are placed to the left of the note head.

They apply to the note on which they are placed and to subsequent similar notes in the same measure and octave. In modern notation they do not apply to notes in other octaves, but this was not always the convention. To cancel an accidental later in the same measure and octave, another accidental such as a natural (♮) or a sharp (♯) may be used.

Other notation and usage
[edit]- Historically, raising a double flat to a single flat would be notated using a natural and flat sign (♮♭) or vice-versa (♭♮) instead of the conventional flat sign (♭). In modern notation the leading natural sign is often omitted. The similar principle of the natural sign notation can apply when canceling a triple flat or beyond. The combination ♮♯ can be also written when changing a flat to a sharp.
- In environments where the
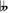 symbol is not supported, or in specific text notation, a double flat can be written as ♭♭, two lower-case b's (bb), etc. Likewise, a triple flat can also be written as ♭♭♭, etc.[citation needed]
symbol is not supported, or in specific text notation, a double flat can be written as ♭♭, two lower-case b's (bb), etc. Likewise, a triple flat can also be written as ♭♭♭, etc.[citation needed] - In environments where the
 or 𝄳 symbol is not supported, or in specific text notation, a half flat can be written as d, etc. Likewise, a flat and a half can also be written as d♭, db, etc.[citation needed]
or 𝄳 symbol is not supported, or in specific text notation, a half flat can be written as d, etc. Likewise, a flat and a half can also be written as d♭, db, etc.[citation needed] - To allow extended just intonation, composer Ben Johnston uses a flat as an accidental to indicate a note is lowered 70.6 cents.[5]
Unicode
[edit]The Unicode character ♭ (U+266D) can be found in the block Miscellaneous Symbols; its HTML entity is ♭. Other assigned flat signs are as follows:
- U+1D12B 𝄫 MUSICAL SYMBOL DOUBLE FLAT
- U+1D133 𝄳 MUSICAL SYMBOL QUARTER TONE FLAT
Footnotes
[edit]- ^ For example, in quarter-comma meantone a flat always lowers a note's pitch by 76.05 cents, and in just intonation a flat commonly lowers a note's pitch by 70.57 cents. These are smaller intervals than the 100 cents lower used in 12 TET, and the 113.7 cents lower used in Pythagorean tuning. In well temperaments, a flat is two or more different sizes, depending on the temperament and where the unaltered note sits on the circle of fifths.
- ^ a b
For example, in 53 TET sharps and flats have two or three different sub-levels, and notation for flattening notes varies, but usually involves several different symbols; one of the sets of 53 TET flat symbols is ♭ (67.9 cents),
 (45.3 cents), and ↓ (22.6 cents), used both separately and in combinations.
(45.3 cents), and ↓ (22.6 cents), used both separately and in combinations.
- ^ The size of the lowering of pitch by a "comma" varies, depending on the tuning system; it is normally 21 + 1 / 2 cents but can vary between 20–25 cents.[b]
- ^ 12 TET is the predominant system of tuning in Western music.
See also
[edit]- Electronic tuner – Device used to tune musical instruments
References
[edit]- ^ Benward & Saker (2003). Music in Theory and Practice. Vol. 1 (7th ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 6.
Flat (♭) lowers the pitch a half step.
- ^ Flat. Glossary. Naxos Records. Archived from the original on 2021-07-15. Retrieved 2015-02-06.
- ^ Byrd, Donald (October 2018). "Extremes of conventional music notation". luddy.indiana.edu. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University.
- ^ "B-triple-flat note". Retrieved March 11, 2025.
- ^ Fonville, J. (Summer 1991). "Ben Johnston's extended just intonation – a guide for interpreters". Perspectives of New Music. 29 (2): 106–137.
... the 25 / 24 ratio is the sharp (♯) ratio ... this raises a note approximately 70.6 cents.(p 109)
External links
[edit] Media related to Flats (music) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Flats (music) at Wikimedia Commons